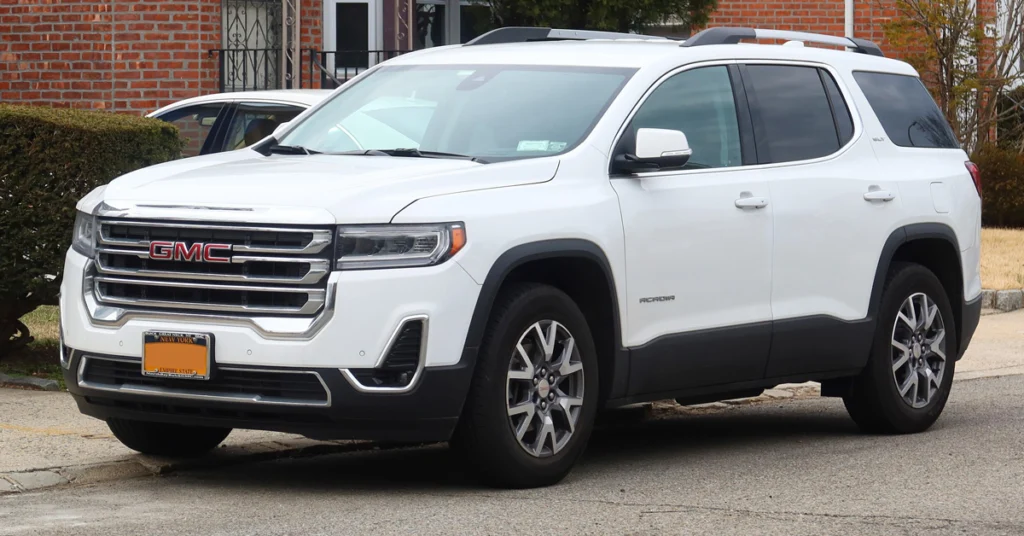
The GMC Acadia has been a familiar name in the SUV and crossover market for almost two decades. Loved for its spacious interiors, versatile seating, and family-friendly features, it has been a strong contender for those who want comfort, style, and utility in one package. At the same time, it has earned a reputation for a mix of mechanical quirks and recurring issues. From its early days as a larger, unibody SUV to the lighter, modern redesign, the Acadia has had its fair share of ups and downs.
If you’re considering buying one or already own an Acadia, understanding common problems from engine and transmission issues to electrical and power steering quirks can help you avoid surprises and ensure your vehicle remains dependable. In this guide, we’ll cover the Acadia’s history, reliability trends, and what to watch out for to keep your SUV running smoothly on UAE roads.
GMC Acadia Overview and Evolution
The Acadia was introduced in 2006, designed to replace older models such as the GMC Safari, Pontiac Montana SV6, and GMC Envoy. Built on GM’s Lambda platform, it shared components with the Chevrolet Traverse, Buick Enclave, and Saturn Outlook. This shared platform allowed GM to combine parts efficiency with varied styling and features for different brands.
First Generation (2007–2016)
GMC’s first unibody SUV offered seating for up to eight people, appealing to large families or those needing extra cargo space. Front- or all-wheel drive options were available, and the standard engine was a 3.6-liter V6 producing up to 310 horsepower.
However, early models were not without their problems. Recalls affected engine mounts and cargo area rivets, while other technical service bulletins (TSBs) addressed transmission and electrical issues. Despite these early hiccups, many owners appreciated the spacious interior, smooth ride, and towing capability.
Second Generation (2017–Present)
In 2017, GMC introduced a lighter, more compact Acadia, trimming roughly 700 kilograms compared to its predecessor. The redesign included 5-, 6-, or 7-seat configurations, aiming to balance family utility with easier city driving. Engine choices included a 2.0-liter turbocharged four-cylinder for efficiency and a 3.6-liter V6 for those wanting more power. Transmission options expanded to a 6-speed automatic or a 9-speed dual-clutch unit, offering smoother shifts and improved fuel efficiency.
The second-generation Acadia also received updated infotainment systems, advanced driver assistance features, and better interior materials, though some electrical and minor mechanical problems persist, as we’ll explore below.
Understanding GMC Acadia Reliability
Compared to competitors like the Ford Edge, Toyota Highlander, or Honda Pilot, the Acadia tends to land in the middle of the pack in reliability. It’s not the worst SUV on the market, but it does require attentive maintenance, particularly on older first-generation models.
Critical Reliability Ratings
- The 2020 Acadia received below-average reliability scores from U.S. News and J.D. Power.
- Owners commonly report rattling, squeaks, and electrical glitches affecting infotainment screens, dashboard displays, and sometimes even engine warning lights.
Recalls and Technical Service Bulletins
Across its production history, the Acadia has undergone more than 20 recall campaigns and nearly 2,000 TSBs. Engine and transmission issues are the most frequently cited concerns, followed by power steering, suspension, and minor electrical problems. Awareness of these recalls and bulletins can save future owners significant time and money.
Most Common GMC Acadia Problems by Model Year
First-Generation Issues (2007–2016)
- Transmission Failures
Many first-gen Acadias suffered from cracked wave plates or metal shavings in the transmission fluid, leading to stalling or complete gearbox failure. Problems could appear as early as 75,000 km and often required expensive repairs. - Engine Problems
Timing chain failures, leaking gaskets, and catalytic converter issues were frequent. Warning lights could appear suddenly, and some engines required full replacement after sustained damage. - Power Steering Failures
Pump and rack failures made low-speed turns and parking maneuvers difficult and potentially unsafe. Regular fluid checks and early replacement of worn components can prevent sudden failure. - Air Conditioning and Electrical Glitches
Leaks, faulty wiring, and sensor errors caused inconsistent cabin cooling and dashboard alerts. While not always immediately dangerous, these issues can affect comfort and add repair costs over time.
Second-Generation Issues (2017–Present)
- Shift to Park Errors
Some drivers report difficulty engaging “Park,” which can occasionally drain the battery if left unresolved. - Minor Electrical and A/C Problems
Infotainment system glitches, sensor failures, and occasional air conditioning inefficiency continue to appear but are generally easier and less costly to fix compared to first-generation issues.
Detailed Breakdown of Frequent Problems
Even newer models aren’t immune to wear and tear. Here’s what to monitor:
- Overheating: Malfunctioning thermostats, radiator blockages, or contaminated coolant can cause engine overheating. In the UAE, extreme heat makes cooling system maintenance essential.
- Fuel Gauge Inaccuracies: Faulty sensors or wiring problems can misreport fuel levels, increasing the risk of running out unexpectedly, especially during long drives outside city limits.
- Suspension Issues: Worn struts, stabilizer links, or control arms can produce noise over bumps, compromise handling, and reduce ride comfort.
- Brake Concerns: Squeaking or reduced braking performance usually indicates worn pads or degraded brake fluid. Proactive brake maintenance ensures safety on Dubai’s highways and urban streets.
- Ignition and Battery Problems: Faulty ignition switches or parasitic battery drains can prevent starting, especially after short trips or when parked for extended periods.
- Water Leaks: Blocked sunroof drains or degraded door seals may allow water into the cabin, usually near footwells. In coastal areas like Abu Dhabi, even small leaks can accelerate corrosion if ignored.
Tips for GMC Acadia Owners and Buyers
- Always get a full inspection before purchasing, especially for first-generation models.
- Check transmission fluid and listen for unusual noises during gear shifts.
- Maintain timing chains and power steering systems proactively.
- Keep an eye on electrical systems, including infotainment, dashboard alerts, and sensors.
- Follow a consistent maintenance schedule, including coolant, brake fluid, and suspension checks, to extend the life of your Acadia.
- Use high-quality fluids and genuine GM parts when possible to avoid recurring issues.
GMC Acadia Years to Approach with Caution
- First Generation (2007–2016): High prevalence of engine and transmission failures makes these models riskier for buyers. Inspections should focus on the engine, transmission, power steering, and suspension.
- Recent Models (2017–2021): Generally more reliable, though minor electrical and shift-to-park issues may still arise. Keeping software updated and monitoring for alerts is important.
UAE & Dubai Insights
In the UAE, where summer temperatures can exceed 45°C and road conditions vary from smooth highways to desert tracks, maintaining your GMC Acadia is essential. Regular inspections of the cooling system, power steering, and air conditioning can prevent breakdowns and ensure cabin comfort in extreme heat.
MotorHub connects drivers with trusted workshops across Dubai and Abu Dhabi, offering expert service, quick repairs, and proactive maintenance. Whether you own a first-generation Acadia or a newer model, addressing minor issues promptly and following a consistent maintenance routine is the key to safe, reliable driving on Emirates roads.
From checking coolant levels to monitoring electrical alerts, a little preventive care can go a long way. With the right attention, your GMC Acadia can remain a comfortable, dependable SUV for years to come.